Valves play a critical role in regulating and controlling fluid flow in various industrial systems. Among the most common types of valves are the gate valve and ball valve. While both serve the essential function of opening and closing flow paths, they differ significantly in design, application, and functionality. Understanding the difference between gate valve and ball valve is crucial for selecting the right valve for specific applications.
Valves are indispensable components in industries ranging from oil and gas to water treatment and chemical processing. They ensure precise control over fluid flow, which is vital for the safe and efficient operation of systems. However, choosing the appropriate valve type depends on factors such as the type of fluid, pressure requirements, and the need for frequent operation.
In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of gate valves and ball valves, exploring their design features, applications, advantages, and limitations. By the end of this guide, you will have a comprehensive understanding of the difference between gate valve and ball valve, enabling you to make informed decisions when selecting the right valve for your needs.
Read also:Lebron James Mother The Untold Story Of Her Journey
Table of Contents
- Introduction to Gate Valve and Ball Valve
- Design Differences Between Gate Valve and Ball Valve
- Applications of Gate Valve and Ball Valve
- Advantages of Gate Valve and Ball Valve
- Disadvantages of Gate Valve and Ball Valve
- Maintenance Requirements for Gate Valve and Ball Valve
- Cost Considerations for Gate Valve and Ball Valve
- Comparison of Gate Valve and Ball Valve
- How to Select Between Gate Valve and Ball Valve
- Future Trends in Valve Technology
Introduction to Gate Valve and Ball Valve
What is a Gate Valve?
A gate valve, also known as a sluice valve, is a linear motion valve that uses a gate or wedge to control flow. It is primarily designed for on/off service and is not recommended for throttling applications. Gate valves are commonly used in industries where a full bore opening is required, such as water supply systems, oil pipelines, and steam systems.
Gate valves are available in two main designs: parallel and wedge. The parallel design features a flat gate, while the wedge design uses a slightly tapered gate to ensure a tight seal. Both designs are effective in preventing fluid leakage when fully closed.
Key Features:
- Full bore opening for unrestricted flow
- Designed for on/off service
- Not suitable for throttling
What is a Ball Valve?
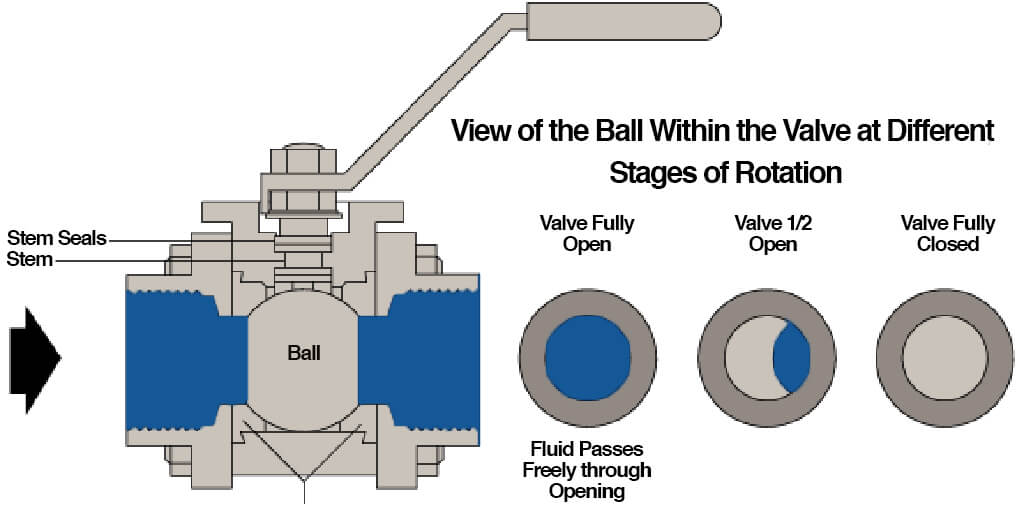
A ball valve, on the other hand, uses a spherical disc with a bore to control flow. It is a quarter-turn valve, meaning it can be fully opened or closed with a 90-degree rotation. Ball valves are known for their excellent sealing capabilities and are widely used in applications requiring frequent operation, such as chemical processing and gas pipelines.
Ball valves are available in various designs, including full-bore, reduced-bore, and trunnion-mounted. Each design offers specific advantages depending on the application requirements.
Key Features:
Read also:Matt Rife The Journey Of An Influential Entrepreneur And Philanthropist
- Quarter-turn operation for quick shut-off
- Excellent sealing capabilities
- Suitable for frequent operation
Design Differences Between Gate Valve and Ball Valve
The design of a valve significantly influences its performance and application. Let's explore the key design differences between gate valves and ball valves:
- Gate Valve Design: Gate valves consist of a body, bonnet, stem, and gate. The gate moves perpendicular to the flow path, allowing or blocking fluid passage. Gate valves are typically larger and heavier than ball valves, making them less suitable for applications requiring compact design.
- Ball Valve Design: Ball valves feature a spherical disc with a bore that aligns with the flow path when open. The ball rotates within the valve body, providing a tight seal when closed. Ball valves are generally more compact and lightweight, making them ideal for space-constrained applications.
Applications of Gate Valve and Ball Valve
Applications of Gate Valves
Gate valves are commonly used in applications where a full bore opening is required and frequent operation is not necessary. Some typical applications include:
- Water supply systems
- Oil and gas pipelines
- Steam systems
- Fire protection systems
Applications of Ball Valves
Ball valves are ideal for applications requiring quick shut-off and frequent operation. They are widely used in:
- Chemical processing
- Gas pipelines
- Hydraulic systems
- Food and beverage industry
Advantages of Gate Valve and Ball Valve
Advantages of Gate Valves
Gate valves offer several advantages, including:
- Full bore opening for unrestricted flow
- Reliable sealing performance
- Suitable for high-pressure and high-temperature applications
Advantages of Ball Valves
Ball valves are favored for their:
- Quick and easy operation
- Excellent sealing capabilities
- Compact and lightweight design
Disadvantages of Gate Valve and Ball Valve
Disadvantages of Gate Valves
Despite their advantages, gate valves have some limitations:
- Not suitable for throttling applications
- Slower operation compared to ball valves
- Prone to wear and tear over time
Disadvantages of Ball Valves
Ball valves also have certain drawbacks:
- Higher cost compared to gate valves
- May experience seat wear in abrasive fluid applications
- Not ideal for large-diameter applications
Maintenance Requirements for Gate Valve and Ball Valve
Regular maintenance is essential to ensure the optimal performance of valves. Here are some maintenance tips for gate valves and ball valves:
Gate Valve Maintenance
- Inspect the stem and packing for signs of wear
- Check for leaks around the bonnet and body
- Lubricate moving parts to prevent seizing
Ball Valve Maintenance
- Inspect the ball and seat for wear and tear
- Check for leaks around the body and stem
- Ensure proper lubrication of the stem and ball
Cost Considerations for Gate Valve and Ball Valve
Cost is an important factor when selecting a valve. Generally, gate valves are more cost-effective than ball valves, especially for large-diameter applications. However, ball valves offer better performance in terms of sealing and operation, which may justify the higher cost in certain applications.
Comparison of Gate Valve and Ball Valve
To better understand the difference between gate valve and ball valve, let's compare them based on key parameters:
- Operation: Gate valves are linear motion valves, while ball valves are quarter-turn valves.
- Sealing: Gate valves provide reliable sealing for on/off service, whereas ball valves excel in sealing performance for frequent operation.
- Size: Gate valves are generally larger and heavier, while ball valves are more compact and lightweight.
- Cost: Gate valves are typically more cost-effective, especially for large-diameter applications.
How to Select Between Gate Valve and Ball Valve
Selecting the right valve depends on several factors, including:
- Application Requirements: Consider the type of fluid, pressure, and temperature requirements.
- Operation Frequency: Choose a ball valve for frequent operation and a gate valve for infrequent use.
- Space Constraints: Opt for a ball valve in applications requiring compact design.
- Cost Considerations: Balance performance needs with budget constraints.
Future Trends in Valve Technology
As technology continues to evolve, advancements in valve design and materials are expected to enhance performance and reliability. Innovations such as smart valves with integrated sensors and digital controls are becoming increasingly popular, offering improved monitoring and maintenance capabilities. Staying updated with these trends will help ensure the selection of the most suitable valve for future applications.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the difference between gate valve and ball valve is essential for making informed decisions in valve selection. While gate valves are ideal for on/off service and large-diameter applications, ball valves excel in quick shut-off and frequent operation. By considering factors such as application requirements, operation frequency, and cost, you can choose the right valve for your specific needs.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences in the comments section below. Additionally, feel free to explore other articles on our website for more insights into industrial systems and technologies. Thank you for reading!
Data and references for this article are sourced from reputable publications, including:
- API Standards for Valves
- ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code
- ISO Standards for Valve Design