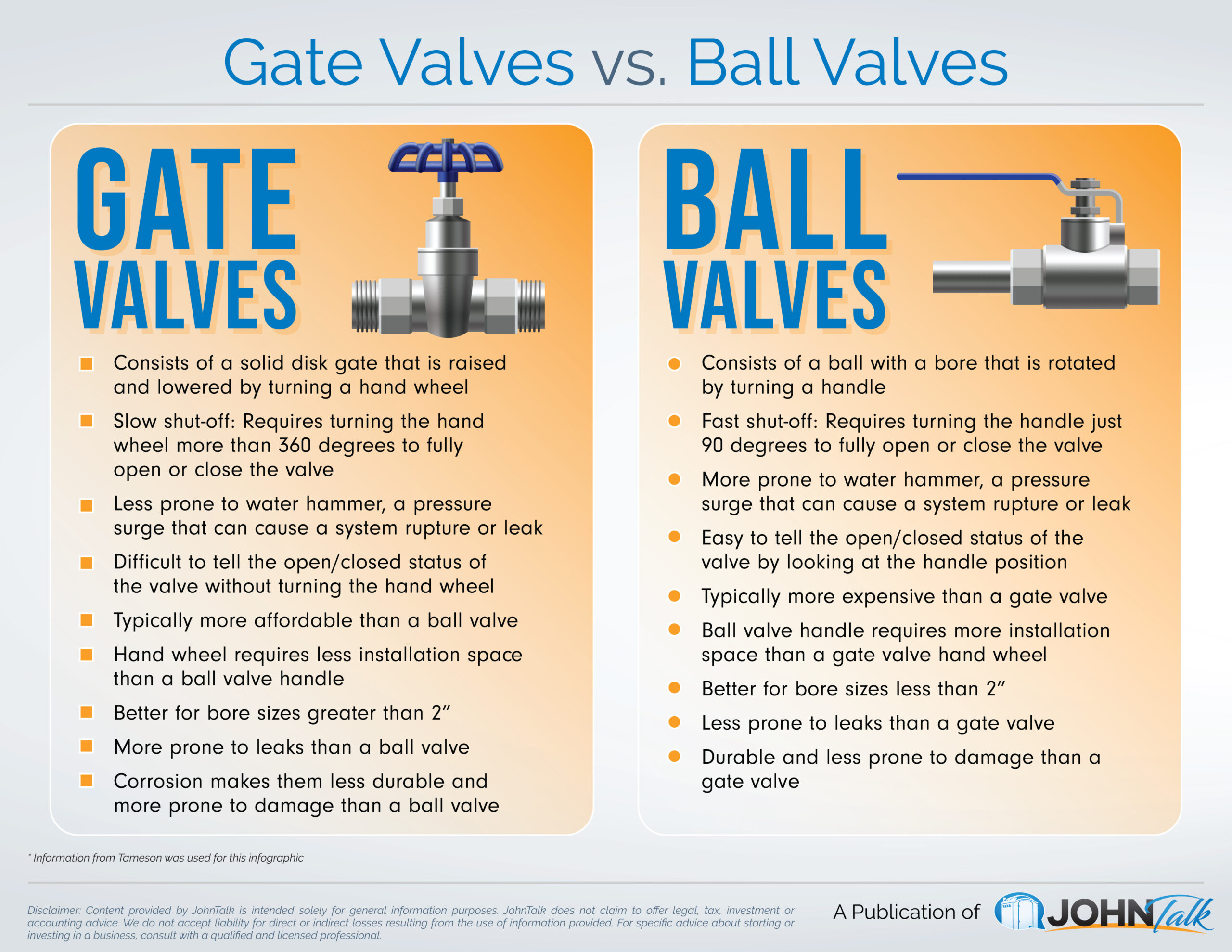
When it comes to choosing between a ball valve or gate valve, understanding their differences and applications is crucial for any plumbing or industrial project. Both valves serve the purpose of controlling fluid flow, but their designs and characteristics make them suitable for specific scenarios. This article will guide you through the nuances of ball valves and gate valves, helping you make an informed decision.
Valves are essential components in fluid systems, ensuring efficient control and regulation of flow. Whether you're dealing with water, gas, or other media, selecting the right valve can significantly impact system performance and longevity. With so many options available, it's easy to get overwhelmed.
In this comprehensive guide, we'll explore the features, advantages, and disadvantages of ball valves and gate valves. By the end, you'll have a clear understanding of which valve type best suits your needs. Let's dive in!
Read also:Dylan Paul Conner Rising Star In The Entertainment Industry
Table of Contents
- Introduction to Ball Valve and Gate Valve
- Structural Differences Between Ball Valve and Gate Valve
- Applications of Ball Valve and Gate Valve
- Performance Comparison: Ball Valve vs. Gate Valve
- Maintenance Requirements
- Cost Considerations
- Factors to Consider When Selecting Between Ball Valve or Gate Valve
- Longevity and Durability
- Industry Standards and Certifications
- Conclusion and Final Thoughts
Introduction to Ball Valve and Gate Valve
Ball valves and gate valves are two of the most commonly used valves in various industries. Both are designed to control fluid flow, but their mechanisms and applications differ significantly. A ball valve uses a rotating ball with a hole in the middle to control the flow, while a gate valve uses a sliding gate to open or close the passage.
Ball valves are known for their quick on/off capabilities and excellent sealing properties, making them ideal for applications requiring frequent operation. On the other hand, gate valves are better suited for applications where the valve needs to remain open or closed for extended periods.
Understanding the fundamental differences between these two valve types is essential for selecting the right one for your project. Let's delve deeper into their structural differences.
Structural Differences Between Ball Valve and Gate Valve
At the heart of every valve lies its design, which dictates its functionality and performance. Ball valves and gate valves differ significantly in their internal structure and mechanism.
Ball Valve Structure
A ball valve consists of a spherical disc with a port or hole in the middle. The ball rotates within the valve body, aligning the hole with the inlet and outlet ports to allow or block fluid flow. Ball valves are typically available in two main types: floating ball valves and trunnion-mounted ball valves.
- Floating Ball Valve: The ball is supported by the upstream pressure and can move slightly within the valve body.
- Trunnion-Mounted Ball Valve: The ball is fixed in place with a trunnion, providing better stability and reducing wear and tear.
Gate Valve Structure
Gate valves operate by raising or lowering a gate or wedge to control the flow. The gate is attached to a stem that moves up or down when the handwheel is turned. Gate valves are available in two primary designs: rising stem and non-rising stem.
Read also:Is Mase A Pastor Exploring The Truth Behind His Spiritual Journey
- Rising Stem Gate Valve: The stem rises above the valve body, providing a visual indication of the valve's position.
- Non-Rising Stem Gate Valve: The stem remains within the valve body, making it suitable for applications where space is limited.
Applications of Ball Valve and Gate Valve
The choice between a ball valve or gate valve often depends on the specific application. Each valve type excels in different scenarios due to its unique characteristics.
Ball Valve Applications
Ball valves are ideal for applications requiring quick shut-off and reliable sealing. They are commonly used in:
- Pipeline systems for water, gas, and oil
- Chemical and petrochemical industries
- Fire protection systems
- Residential plumbing systems
Gate Valve Applications
Gate valves are better suited for applications where the valve needs to remain open or closed for extended periods. They are often used in:
- Water treatment plants
- Power generation facilities
- Pipeline systems for large-scale industrial applications
- Steam systems
Performance Comparison: Ball Valve vs. Gate Valve
When comparing the performance of ball valves and gate valves, several factors come into play, including flow control, pressure rating, and temperature resistance.
Ball valves offer excellent sealing capabilities and can handle high-pressure and high-temperature applications. They are also easier to operate, requiring less torque to open or close. However, they may not be suitable for throttling applications due to potential wear on the ball and seat.
Gate valves, on the other hand, are better suited for applications requiring full-bore flow. They can handle larger pipe sizes and are ideal for applications where minimal pressure drop is desired. However, they are not recommended for frequent operation due to potential wear on the gate and seat.
Maintenance Requirements
Maintenance is a critical aspect of valve longevity and performance. Both ball valves and gate valves require regular inspection and maintenance to ensure optimal operation.
Ball valves typically require less maintenance due to their simple design and fewer moving parts. However, they may need periodic lubrication and inspection of the ball and seat for wear and tear.
Gate valves, with their more complex mechanism, may require more frequent maintenance. The gate and seat should be inspected regularly for signs of corrosion or damage, and the stem packing should be replaced as needed.
Cost Considerations
The cost of ball valves and gate valves can vary significantly based on factors such as size, material, and application. Generally, ball valves are more cost-effective for smaller pipe sizes and applications requiring quick shut-off. Gate valves, while more expensive upfront, may be more economical for larger pipe sizes and applications where full-bore flow is desired.
When considering cost, it's important to factor in the long-term maintenance and replacement costs. Ball valves, with their longer lifespan and lower maintenance requirements, may offer better value in the long run.
Factors to Consider When Selecting Between Ball Valve or Gate Valve
Selecting the right valve for your application involves considering several factors, including:
- Pipe size and system pressure
- Fluid type and temperature
- Frequency of operation
- Space constraints
- Cost and budget considerations
For example, if you're working on a residential plumbing project, a ball valve may be the better choice due to its ease of operation and cost-effectiveness. In contrast, a gate valve may be more suitable for a large-scale industrial application requiring full-bore flow.
Longevity and Durability
The longevity of a valve depends on its material, design, and operating conditions. Ball valves, made from materials such as stainless steel, brass, and PVC, are known for their durability and resistance to corrosion. They can last for decades with proper maintenance.
Gate valves, while equally durable, may experience wear and tear over time due to their more complex mechanism. Regular maintenance and inspection are essential to ensure their longevity and performance.
Industry Standards and Certifications
When selecting a valve, it's important to ensure it meets relevant industry standards and certifications. Both ball valves and gate valves are subject to various standards, including:
- ASME B16.34: Pressure-Containing Shutoff Valves
- API 6D: Pipeline and Pipeline-Related Equipment
- ISO 14313: Petroleum and Natural Gas Industries
Valves certified to these standards have undergone rigorous testing to ensure they meet performance, safety, and quality requirements. Always verify the certifications of the valves you purchase to ensure they meet your application's needs.
Conclusion and Final Thoughts
Choosing between a ball valve or gate valve ultimately depends on your specific application and requirements. Ball valves excel in applications requiring quick shut-off and reliable sealing, while gate valves are better suited for applications where full-bore flow and minimal pressure drop are desired.
By considering factors such as pipe size, fluid type, frequency of operation, and cost, you can make an informed decision that ensures optimal performance and longevity. Remember to adhere to industry standards and certifications to ensure safety and quality.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences in the comments below. Have you used both ball valves and gate valves in your projects? Which one do you prefer and why? Don't forget to explore our other articles for more insights into plumbing and industrial solutions.
References:
- ASME B16.34
- API 6D
- ISO 14313