Understanding the concept of a web browser is crucial in today’s digital world. As internet usage continues to grow, knowing what a web browser is and how it works becomes essential for both casual users and professionals alike. A web browser serves as the gateway to the vast expanse of the internet, enabling users to access websites, view content, and interact with online services effortlessly.
In this article, we will delve deep into the fundamental aspects of web browsers, exploring their purpose, functionality, and importance in our daily lives. Whether you are a beginner or someone looking to enhance your knowledge, this guide will provide you with comprehensive insights into the world of web browsers.
From understanding the history of web browsers to learning about their features and security aspects, we will cover everything you need to know. By the end of this article, you will have a clear understanding of what a web browser is and how it plays a vital role in shaping our online experiences.
Read also:Exploring The Talented World Of Richard Ayoade A Multifaceted Personality
Table of Contents
- Introduction to Web Browsers
- History of Web Browsers
- How Web Browsers Work
- Types of Web Browsers
- Popular Web Browsers
- Features of Modern Web Browsers
- Security and Privacy in Web Browsers
- Web Browser Compatibility
- Tips for Choosing the Right Web Browser
- Future of Web Browsers
Introduction to Web Browsers
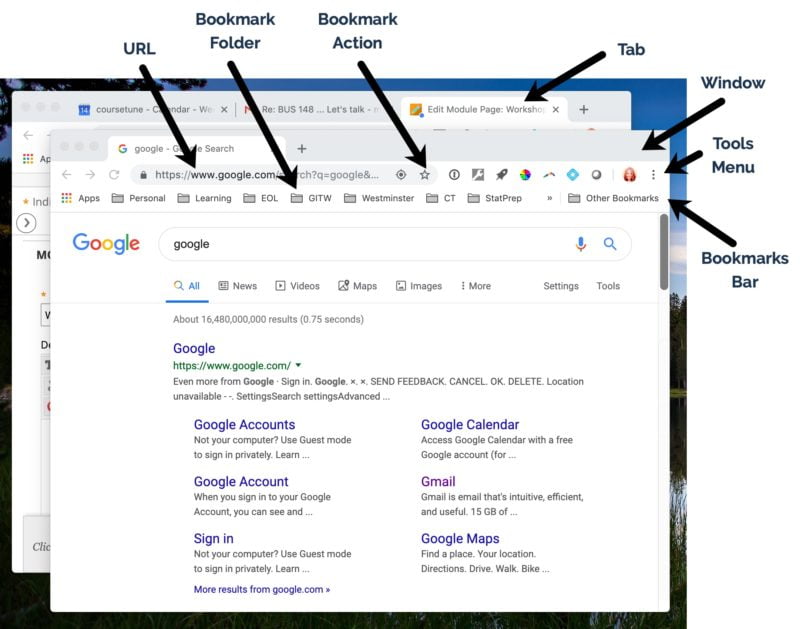
A web browser is a software application designed to access and display content from the World Wide Web. It retrieves data from web servers and presents it in a user-friendly format, allowing users to interact with websites, images, videos, and other digital content. Understanding the basics of a web browser is essential for anyone navigating the internet.
Web browsers have become indispensable tools in our daily lives, enabling us to perform tasks such as online shopping, research, communication, and entertainment. They provide a platform for accessing a wide range of services and applications, making the internet accessible to users of all skill levels.
Why Are Web Browsers Important?
- Web browsers act as the primary interface between users and the internet.
- They simplify the process of accessing and interacting with online content.
- They enhance user experience by offering features like bookmarks, history, and search functionality.
History of Web Browsers
The history of web browsers dates back to the early 1990s when the World Wide Web was first introduced. The first web browser, known as WorldWideWeb, was created by Tim Berners-Lee in 1990. Over the years, web browsers have evolved significantly, with numerous advancements in technology and functionality.
Key Milestones in Web Browser Development
- 1993 – Mosaic: The first widely used web browser that introduced graphical user interface elements.
- 1994 – Netscape Navigator: A groundbreaking browser that dominated the market in the mid-1990s.
- 1995 – Internet Explorer: Released by Microsoft, it became the default browser for Windows users.
- 2003 – Safari: Apple's entry into the web browser market, offering a sleek and user-friendly experience.
- 2008 – Google Chrome: Revolutionized browsing with its speed, simplicity, and innovative features.
How Web Browsers Work
Web browsers function by sending requests to web servers and retrieving data in the form of HTML, CSS, and JavaScript files. Once the data is received, the browser processes it and displays the content on the user's screen. This process involves several components working together seamlessly:
- Rendering Engine: Responsible for interpreting HTML, CSS, and JavaScript to render web pages.
- Network Layer: Handles communication between the browser and web servers.
- User Interface: Provides tools like address bars, tabs, and menus for user interaction.
Steps Involved in Loading a Web Page
- The user enters a URL in the address bar.
- The browser sends an HTTP request to the web server.
- The server responds with the requested files.
- The browser processes the files and displays the web page.
Types of Web Browsers
Web browsers can be categorized based on their functionality, platform compatibility, and target audience. The most common types of web browsers include:
- Desktop Browsers: Designed for use on personal computers and laptops.
- Mobile Browsers: Optimized for smartphones and tablets.
- Specialized Browsers: Tailored for specific tasks like secure browsing or accessibility.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Web Browser
- Performance and speed
- Security features
- Compatibility with devices and operating systems
- User interface and ease of use
Popular Web Browsers
Several web browsers have gained widespread popularity due to their performance, features, and user experience. Some of the most popular web browsers include:
Read also:Data Aries Sign Unveiling The Secrets Of The Zodiac
- Google Chrome: Known for its speed, simplicity, and extensive library of extensions.
- Mozilla Firefox: Offers strong privacy features and customization options.
- Safari: Apple's default browser, optimized for macOS and iOS devices.
- Microsoft Edge: A modern browser with improved performance and compatibility.
Comparison of Popular Web Browsers
Each browser has its strengths and weaknesses, and the choice ultimately depends on individual preferences and needs. For example, Google Chrome excels in speed and extension support, while Mozilla Firefox focuses on privacy and customization.
Features of Modern Web Browsers
Modern web browsers come equipped with a wide range of features designed to enhance user experience. These features include:
- Tabbed Browsing: Allows users to open multiple web pages in a single window.
- Bookmarks: Enables users to save frequently visited websites for quick access.
- Incognito Mode: Provides a private browsing session without saving history or cookies.
- Extensions and Add-ons: Allows users to customize and enhance browser functionality.
Advanced Features in Modern Browsers
In addition to basic features, modern web browsers offer advanced functionalities such as voice search, password managers, and ad blockers. These features aim to make browsing more efficient and secure.
Security and Privacy in Web Browsers
Security and privacy are critical aspects of web browsing. Web browsers employ various measures to protect users from online threats such as malware, phishing, and data breaches. Some of the key security features include:
- HTTPS Encryption: Ensures secure communication between the browser and web servers.
- Popup Blockers: Prevents intrusive ads and malicious pop-ups.
- Tracking Protection: Limits the ability of third-party trackers to monitor user activity.
Best Practices for Secure Browsing
- Keep your browser up to date with the latest security patches.
- Avoid clicking on suspicious links or downloading unknown files.
- Use strong and unique passwords for online accounts.
Web Browser Compatibility
Web browser compatibility refers to the ability of a website or application to function correctly across different browsers. Ensuring compatibility is crucial for developers to provide a consistent user experience. Some common compatibility issues include:
- Differences in rendering engines
- Variations in supported HTML and CSS features
- JavaScript execution discrepancies
Tools for Testing Browser Compatibility
Developers can use tools like BrowserStack and CrossBrowserTesting to test their websites on multiple browsers and devices. These tools help identify and resolve compatibility issues before launching a website.
Tips for Choosing the Right Web Browser
Selecting the right web browser depends on your specific needs and preferences. Consider the following factors when making your decision:
- Performance and speed requirements
- Security and privacy features
- Compatibility with your devices and operating system
- User interface and ease of use
Evaluating Browser Options
Take the time to evaluate different browsers and try them out to see which one suits your needs best. Reading reviews and comparing features can also help in making an informed decision.
Future of Web Browsers
The future of web browsers looks promising, with ongoing advancements in technology and user experience. Some trends to watch out for include:
- Improved artificial intelligence integration for enhanced browsing experiences.
- Greater emphasis on privacy and security features.
- Increased focus on cross-platform compatibility and synchronization.
Emerging Technologies in Web Browsing
New technologies such as WebAssembly and Progressive Web Apps (PWAs) are set to transform the way we interact with web browsers. These innovations promise faster, more secure, and more immersive online experiences.
Conclusion
In conclusion, mastering the basics of what a web browser is and how it works is essential in today’s digital age. From understanding its history and functionality to exploring its features and security aspects, this guide has provided a comprehensive overview of web browsers. By staying informed and choosing the right browser for your needs, you can enhance your online experience and stay safe while browsing.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences in the comments section below. Additionally, feel free to explore our other articles for more insights into technology and digital trends. Thank you for reading!