A rainbow is one of nature's most breathtaking phenomena, captivating people of all ages with its vibrant display of colors. Have you ever wondered about the sequence of colors in a rainbow? This natural wonder follows a specific order that has fascinated scientists and artists alike for centuries. Understanding the science behind rainbows can deepen your appreciation for this marvel of nature.
Rainbows have been the subject of scientific inquiry and artistic inspiration for thousands of years. From ancient myths to modern science, the study of rainbows continues to evolve. The sequence of colors in a rainbow is not random; it follows a precise pattern based on the principles of light refraction and reflection.
This comprehensive guide will take you through everything you need to know about the sequence of colors in a rainbow, including the science behind it, interesting facts, and how rainbows are formed. Whether you're a student, a science enthusiast, or simply curious about the world around you, this article has something for everyone.
Read also:Divas In The Spotlight Exploring The Sensational World Of Onlyfans And Sex Videos
Table of Contents
- What is a Rainbow?
- The Sequence of Colors in a Rainbow
- How Rainbows Are Formed
- The Scientific Explanation
- Double Rainbows: A Rare Phenomenon
- Rainbow Myths and Legends
- Famous Rainbows in History
- Rainbows in Art and Culture
- Rainbows in Modern Science
- Conclusion
What is a Rainbow?
A rainbow is a meteorological phenomenon that occurs when sunlight interacts with raindrops in the atmosphere, creating a spectrum of colors in the sky. It is one of the most beautiful natural displays of light, often appearing after a rainstorm when the sun is shining. The formation of a rainbow involves the principles of refraction, reflection, and dispersion of light.
Types of Rainbows
While the primary rainbow is the most common, there are other types of rainbows that occur under specific conditions:
- Primary Rainbow: The most common type, featuring the sequence of colors in a single arc.
- Double Rainbow: A rare phenomenon where a secondary rainbow appears above the primary one.
- Supernumerary Rainbows: Additional arcs that appear within the primary rainbow, caused by interference patterns.
- Fogbow: A rainbow formed by tiny water droplets in fog, often appearing white or pale.
The Sequence of Colors in a Rainbow
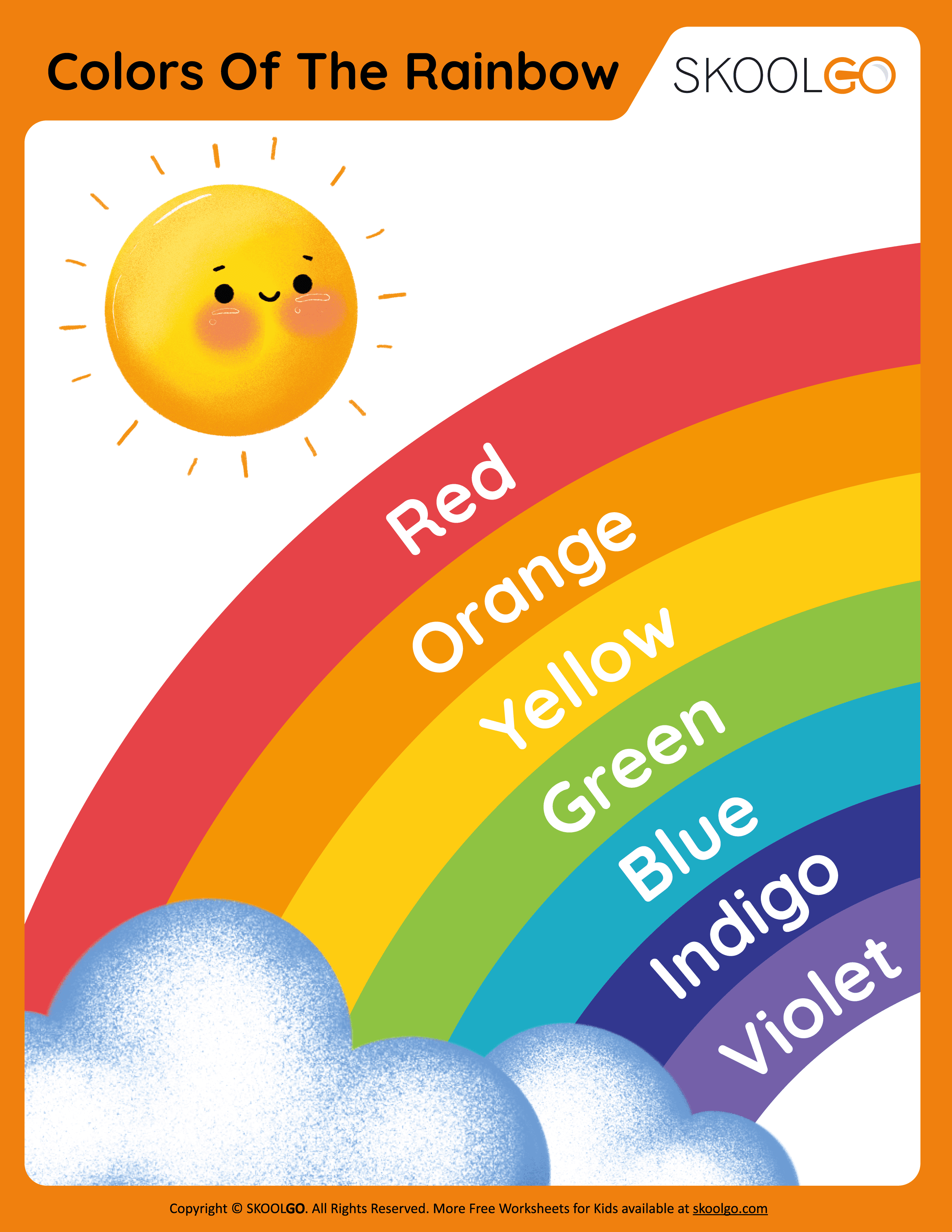
The sequence of colors in a rainbow follows a specific order: Red, Orange, Yellow, Green, Blue, Indigo, and Violet. This sequence is often remembered using the acronym "ROYGBIV." Each color corresponds to a specific wavelength of light, with red having the longest wavelength and violet the shortest.
Why Does the Sequence Matter?
The sequence of colors in a rainbow is determined by the way light is refracted and reflected within raindrops. Longer wavelengths, such as red, are refracted at a shallower angle than shorter wavelengths, such as violet, resulting in the distinct order of colors.
How Rainbows Are Formed
Rainbows are formed when sunlight passes through raindrops in the atmosphere. The process involves three main steps: refraction, reflection, and dispersion.
- Refraction: When sunlight enters a raindrop, it slows down and bends due to the change in medium.
- Reflection: The light is then reflected off the inner surface of the raindrop.
- Dispersion: As the light exits the raindrop, it separates into its constituent colors, creating the spectrum we see as a rainbow.
Conditions for Rainbow Formation
Rainbows are most commonly seen after a rainstorm when the sun is shining. The sun must be behind the observer, and the raindrops must be in front. The angle between the sun, the raindrops, and the observer is critical for the formation of a rainbow, typically around 42 degrees for the primary arc.
Read also:Gavin Casalegnos Wedding Photos A Stunning Celebration
The Scientific Explanation
The science behind rainbows involves the interaction of light with water droplets in the atmosphere. When sunlight enters a raindrop, it undergoes refraction, causing the light to split into its constituent colors. This phenomenon is known as dispersion. The angle at which the light exits the raindrop determines the position of each color in the rainbow.
Key Concepts in Rainbow Formation
Several key concepts explain the formation of rainbows:
- Refraction: The bending of light as it passes from one medium to another.
- Reflection: The bouncing back of light when it hits a surface.
- Dispersion: The separation of light into its constituent colors based on wavelength.
Double Rainbows: A Rare Phenomenon
A double rainbow occurs when a secondary rainbow appears above the primary one. The secondary rainbow is formed by a second reflection of light inside the raindrops, resulting in a reversed sequence of colors. In the secondary rainbow, the colors appear in the opposite order: Violet, Indigo, Blue, Green, Yellow, Orange, and Red.
Why Are Double Rainbows Rare?
Double rainbows are less common because they require specific atmospheric conditions. The secondary reflection inside the raindrops must be strong enough to create a visible arc, which is not always the case. Additionally, the secondary rainbow is dimmer than the primary one, making it harder to see.
Rainbow Myths and Legends
Rainbows have been the subject of myths and legends in cultures around the world. From ancient Greece to Native American folklore, rainbows have been seen as bridges between the earthly and spiritual realms.
Famous Rainbow Legends
- Norse Mythology: In Norse mythology, the rainbow is known as Bifröst, a bridge connecting Earth and Asgard, the realm of the gods.
- Irish Folklore: In Irish folklore, leprechauns are said to hide their pots of gold at the end of a rainbow.
- Aboriginal Mythology: In Australian Aboriginal mythology, the rainbow serpent is a powerful creator spirit associated with water and fertility.
Famous Rainbows in History
Throughout history, there have been several notable rainbows that have captured the imagination of people around the world. One of the most famous rainbows occurred in 2017 in Taiwan, where a rainbow lasted for nearly nine hours, setting a new world record.
Record-Breaking Rainbows
Some rainbows have gained fame for their duration or appearance:
- Taiwan's Nine-Hour Rainbow: In 2017, a rainbow lasted for 8 hours and 58 minutes in Taipei, breaking the previous record.
- Double Rainbow in California: In 2010, a double rainbow in California went viral on social media, sparking a cultural phenomenon.
Rainbows in Art and Culture
Rainbows have inspired countless works of art, literature, and music. From the paintings of J.M.W. Turner to the songs of Judy Garland, rainbows have been a symbol of hope, beauty, and inspiration.
Rainbows in Popular Culture
Some notable examples of rainbows in popular culture include:
- Over the Rainbow: The iconic song from "The Wizard of Oz" has become synonymous with dreams and aspirations.
- Rainbow Flag: The rainbow flag, designed by Gilbert Baker in 1978, has become a symbol of LGBTQ+ pride and equality.
Rainbows in Modern Science
In modern science, rainbows continue to be a subject of study and fascination. Researchers use rainbows to understand the behavior of light and the properties of water droplets. Advances in technology have allowed scientists to capture and analyze rainbows in unprecedented detail.
Applications of Rainbow Science
The study of rainbows has practical applications in fields such as meteorology, optics, and environmental science:
- Meteorology: Rainbows help meteorologists understand weather patterns and atmospheric conditions.
- Optics: The principles of refraction and dispersion are used in the design of lenses and optical instruments.
- Environmental Science: Rainbows can indicate the presence of pollutants or other substances in the atmosphere.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the sequence of colors in a rainbow is a fascinating natural phenomenon that combines science and beauty. From the principles of refraction and dispersion to the myths and legends surrounding rainbows, there is much to learn and appreciate about this wonder of nature. Whether you're marveling at a double rainbow or admiring a single arc, rainbows continue to inspire and delight people of all ages.
Take a moment to observe the next rainbow you see and appreciate the science behind it. Share your thoughts and experiences in the comments below, and don't forget to explore other articles on our site for more fascinating insights into the world around us.